What is Cryptocurrency? A Simple Guide for Beginners

In today’s digital landscape, cryptocurrencies have emerged as a revolutionary form of money that exists purely in the digital realm. But what exactly are these digital assets, how do they work, and why have they captured the world’s attention? This guide breaks down the essentials of cryptocurrency in straightforward terms.
The Essence of Cryptocurrency
A cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual form of money that uses cryptography for security, operates on blockchain technology, and functions independently of central authorities like governments or banks.
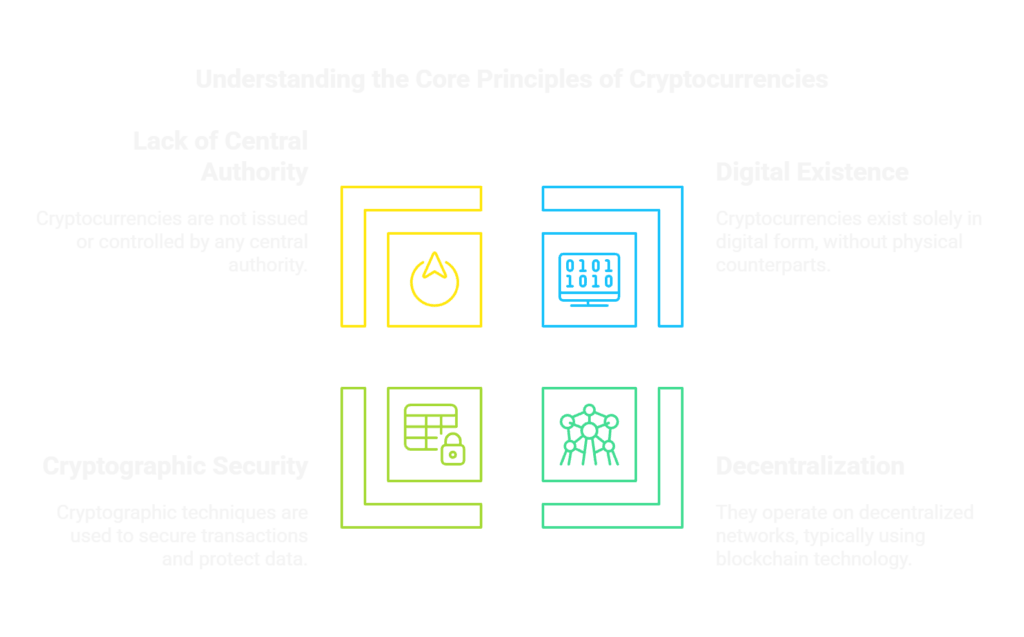
Think of cryptocurrency as digital money that works on a new set of rules—rules enforced by technology and community consensus rather than by governments or financial institutions.
Key Features That Define Cryptocurrencies
What makes cryptocurrencies unique compared to traditional forms of money? Several distinctive characteristics set them apart:
1. Decentralization
Most cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks with no single point of control:
- No central bank or government issues or regulates the currency
- Network participants collectively maintain and secure the system
- Decisions about the currency often require community consensus
2. Limited Supply
Many cryptocurrencies have a capped supply, meaning there’s a maximum number that will ever exist:
- Bitcoin, for example, will never exceed 21 million coins
- This scarcity contrasts with traditional currencies, which can be printed indefinitely
- Limited supply is often built into the cryptocurrency’s code
3. Transparency
Cryptocurrency transactions are recorded on public ledgers:
- Anyone can view transaction history and money flows
- While transactions are visible, user identities remain pseudonymous
- This creates an unprecedented level of financial transparency
4. Borderless Transactions
Cryptocurrencies enable global transactions without traditional barriers:
- Send value anywhere in the world without bank permissions
- Transactions typically process regardless of national boundaries
- International transfers can be faster and cheaper than traditional methods
5. Self-Custody
Cryptocurrencies enable direct ownership without intermediaries:
- Users can maintain complete control of their funds
- No bank or institution needs to hold or manage your assets
- This comes with the responsibility of securing your own digital assets
How Cryptocurrencies Work: The Basics
While the technical details can be complex, the fundamental operation of most cryptocurrencies follows these principles:
Blockchain Foundation
Most cryptocurrencies operate on blockchain technology, which serves as their underlying infrastructure:
- Transactions are grouped into “blocks”
- Blocks are linked chronologically in a “chain”
- This creates an immutable record of all transactions
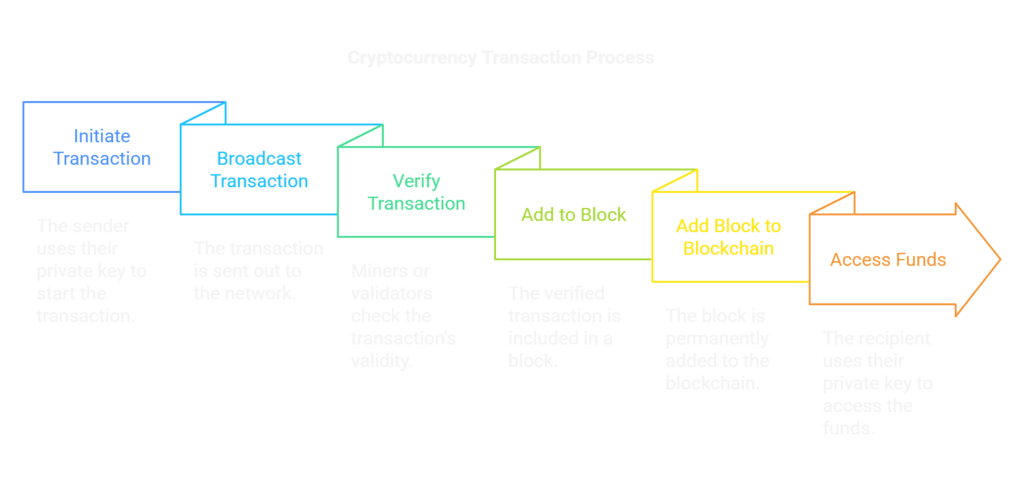
The Transaction Process
Common Types of Cryptocurrencies
The cryptocurrency ecosystem has expanded dramatically since Bitcoin’s creation in 2009:
Bitcoin (BTC)
- The first and most valuable cryptocurrency
- Often called “digital gold” for its store of value properties
- Created by the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto

Ethereum (ETH)
- More than just a currency—it’s a platform for decentralized applications
- Introduced the concept of smart contracts to the blockchain world
- Powers thousands of other tokens and decentralized projects

Stablecoins
- Designed to maintain a stable value, usually pegged to a fiat currency
- Examples include USDC and USDT (pegged to the US dollar)
- Provide stability in the otherwise volatile crypto market

Altcoins
- Any cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin
- Range from serious projects with unique technology to meme coins
- Vary widely in purpose, function, and market adoption
Why Cryptocurrencies Matter
Cryptocurrencies represent more than just a new form of money—they offer a fundamental shift in how we think about value and financial systems:
Financial Inclusion
- Provide banking-like services to the unbanked population
- Require only an internet connection, not a bank account
- Lower barriers to entry for financial services
Monetary Innovation
- Challenge traditional monetary systems and policies
- Experiment with new economic models and incentives
- Create alternatives to inflation-prone fiat currencies
Technological Advancement
- Drive innovation in cryptography, security, and distributed systems
- Spawn new industries like decentralized finance (DeFi)
- Pioneer new models of digital ownership and exchange
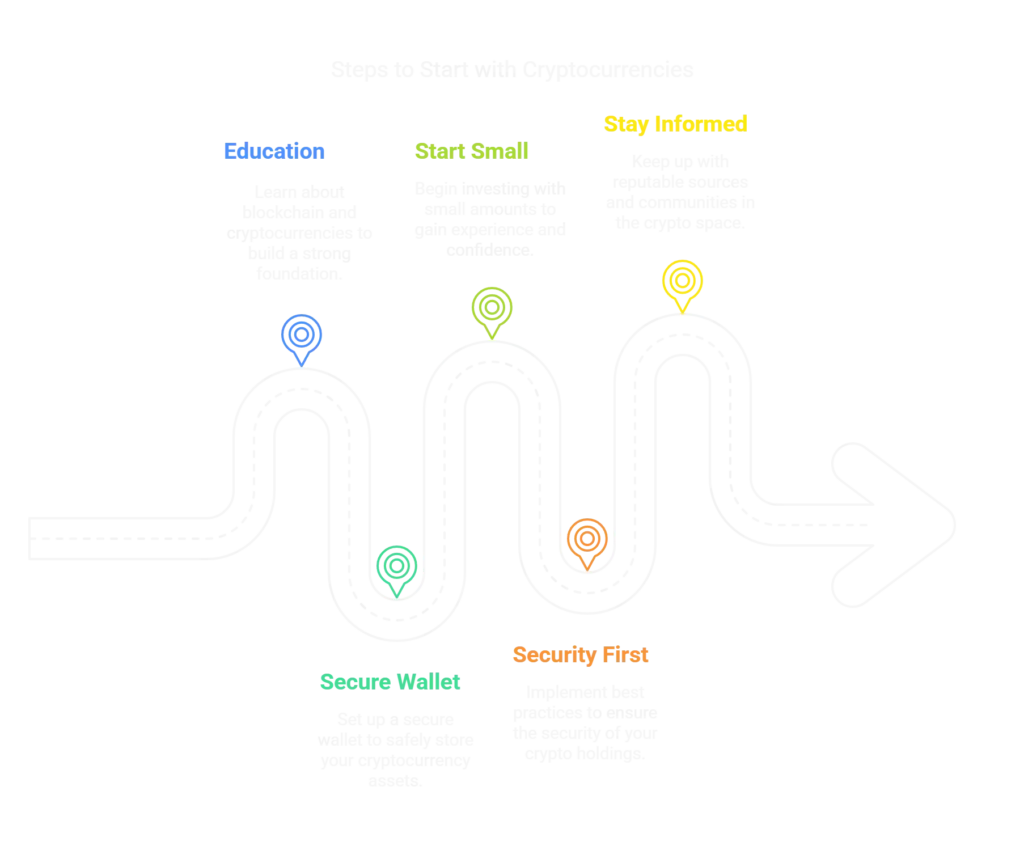
Getting Started with Cryptocurrencies
Common Misconceptions
Despite growing adoption, several misunderstandings about cryptocurrencies persist:
- “Cryptocurrencies are only used for illegal activities” – While early adoption included some illicit use, legitimate applications now dominate the ecosystem
- “Cryptocurrencies have no real value“ – Value derives from utility, scarcity, network effects, and market consensus
- “Cryptocurrencies are just a fad” – The technology has demonstrated staying power and continued development over more than a decade
Looking Forward
As cryptocurrency adoption continues to grow, we can expect:
- Increasing mainstream acceptance and integration
- Evolution of regulatory frameworks
- Technical improvements addressing current limitations
- New applications and use cases we haven’t yet imagined
Cryptocurrencies represent one of the most significant financial innovations of the digital age, with potential impacts extending far beyond just new forms of money. Whether you’re looking to invest, use, or simply understand this technology, grasping these fundamentals provides a solid foundation for navigating the exciting and rapidly evolving world of digital assets.


