Layer 2 Solutions and Lightning Network

Bitcoin’s base layer blockchain excels at security and decentralization but faces limitations in transaction throughput and cost efficiency. Layer 2 solutions address these challenges by building secondary frameworks atop Bitcoin’s main chain, with the Lightning Network emerging as the most promising scaling solution. This article explores how Layer 2 solutions work, the Lightning Network’s architecture, and the evolving ecosystem of Bitcoin scalability.
Understanding Bitcoin's Scaling Challenge
Bitcoin's Base Layer Constraints
- Block Size Limitation: Bitcoin blocks are limited to approximately 1MB (or 4MB with Segregated Witness)
- Block Time Target: New blocks are produced on average every 10 minutes
- Transaction Throughput: These constraints limit Bitcoin to roughly 3-7 transactions per second
- Fee Market: Limited block space creates competition for inclusion, driving up fees during periods of high demand
The Blockchain Trilemma
Bitcoin’s design prioritizes security and decentralization over raw throughput, embracing what’s known as the “blockchain trilemma”:
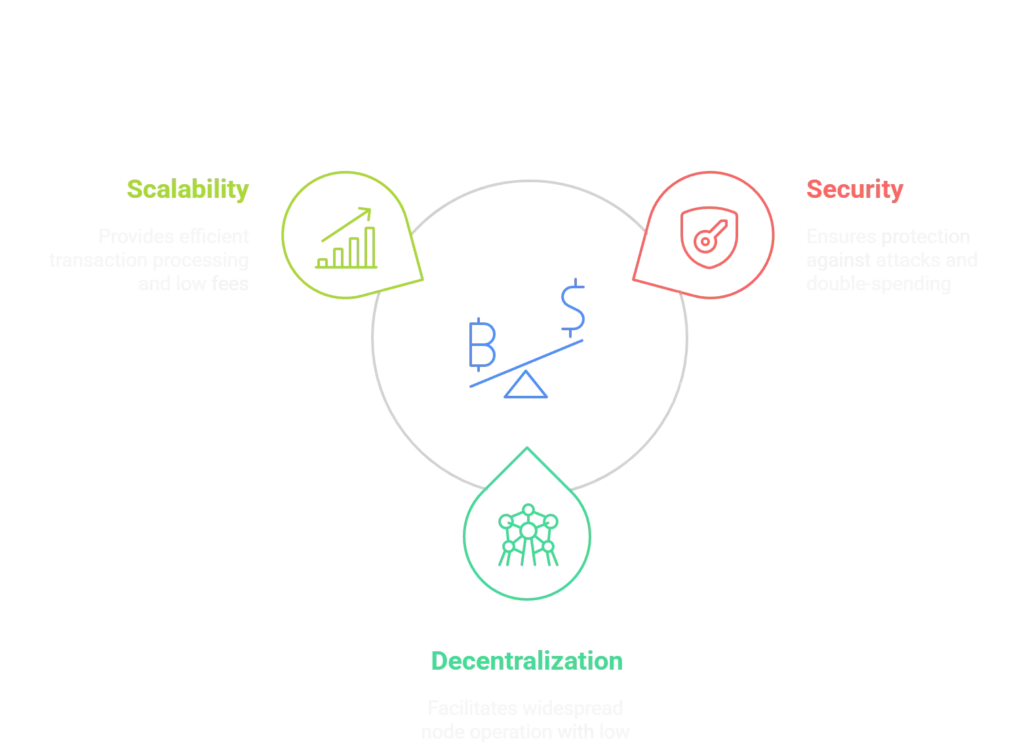
Optimizing for all three simultaneously presents significant challenges. Layer 2 solutions offer a path to enhance scalability while preserving the security and decentralization of the base layer.
What Are Layer 2 Solutions?
- Processing transactions off the main blockchain
- Periodically settling the final state back to the main chain
- Reducing the burden on the base layer
- Leveraging the security of the underlying blockchain
The Layer 2 Approach to Scaling
- Lock funds in a special contract or mechanism on the base layer
- Conduct numerous transactions on the secondary layer
- Settle the final state back to the base layer when needed
The Lightning Network Explained
Core Concepts of Lightning
- Payment Channels
At its foundation, Lightning uses bidirectional payment channels:- Two parties create a channel by committing funds to a special multisignature address on the Bitcoin blockchain
- Once established, they can conduct unlimited transactions between themselves without touching the blockchain
- Each transaction updates the balance allocation within the channel
- Only the channel opening and closing transactions appear on the Bitcoin blockchain
-
Hash Time-Locked Contracts (HTLCs)
HTLCs enable the routing of payments across multiple channels:- They use cryptographic hash functions to lock funds until a secret is revealed
- Time locks ensure funds don’t remain locked indefinitely
- These mechanisms create trustless payment paths across the network
- Routing Network
The true power of Lightning emerges from its network effect:- Users don’t need direct channels with everyone they transact with
- Payments can route through multiple connected channels
- This creates a mesh network where any participant can pay any other participant
- Routing nodes can collect small fees for facilitating transactions
How Lightning Transactions Work
- Path Discovery: The sender’s wallet finds a route through connected channels to reach the recipient
- HTLC Creation: A series of HTLCs are established along the payment path
- Secret Revelation: The recipient claims the payment by revealing the preimage to a cryptographic hash
- Settlement Propagation: The revealed secret propagates back through the path, settling each hop
- Channel Updates: All channels along the path update their balance states
Advantages of the Lightning Network
1. Speed and Cost Efficiency
- Near-Instant Settlements: Transactions confirm in milliseconds to seconds
- Microtransactions: Fees are so low that even tiny payments become economical
- High Throughput: Theoretical capacity of millions of transactions per second
2. Privacy Enhancements
- Improved Transaction Privacy: Not all transactions are visible on the public blockchain
- Reduced Footprint: Less information leakage about payment patterns
- Routing Anonymization: Multi-hop payments obscure the connection between sender and receiver
3. Smart Contract Capabilities
- Conditional Payments: More complex conditions than base layer Bitcoin
- Discreet Log Contracts (DLCs): Enables smart contract functionality without revealing details on-chain
- Atomic Multipath Payments (AMPs): Splitting large payments across multiple channels
Current State of the Lightning Network
Network Capacity and Growth
- Public Capacity: Over 5,000 BTC locked in channels (worth hundreds of millions of dollars)
- Node Count: Tens of thousands of nodes participate in the network
- Channel Connections: Hundreds of thousands of open payment channels
- Transaction Volume: Estimated millions of transactions monthly
Lightning Network Implementations
- LND (Lightning Network Daemon): Developed by Lightning Labs
- c-lightning: Created by Blockstream
- Eclair: Built by ACINQ
- LDK (Lightning Development Kit): A flexible library for custom implementations
User Experience Improvements
- Simplified Channel Management: Automatic channel opening and balancing
- Liquidity Services: Third-party services that provide inbound liquidity
- Mobile Wallets: Numerous non-custodial options for everyday users
- Web Integration: Website plugins for accepting Lightning payments
Other Bitcoin Layer 2 Solutions
Sidechains
- Liquid Network: A sidechain focused on trading and settlement between exchanges
- RSK (Rootstock): Brings Ethereum-like smart contract functionality to the Bitcoin ecosystem
- Key Differences from Lightning: Sidechains have their own consensus mechanisms and block production
Statechains
- Users can transfer full custody of a Bitcoin UTXO without an on-chain transaction
- Particularly useful for transferring exact amounts without change outputs
- Provides complementary benefits to Lightning’s payment channel model
Federated Protocols
- Rely on trusted federations to validate transactions
- Offer speed and convenience at some cost to trustlessness
- Examples include Liquid Network (which is both a sidechain and federated)
Technical Challenges and Solutions
1. Liquidity Management
- Channel Factories: Allow multiple channels to be created with a single on-chain transaction
- Liquidity Marketplaces: Services that connect those needing liquidity with those providing it
- Submarine Swaps: Enable exchanging on-chain and off-chain Bitcoin seamlessly
2. Routing Complexity
- Improved Pathfinding Algorithms: More efficient routing strategies
- Routing Hints: Additional information to help senders find paths
- Trampoline Routing: Delegating path-finding to specialized nodes
3. Channel Management
- Autopilot: Automatic channel management
- Splicing: Adding or removing funds from channels without closing them
- Watchtowers: Third-party services that monitor channels for attempted fraud
Integration with Bitcoin Protocol Upgrades
1. Segregated Witness (SegWit)
- Implemented in 2017
- Fixed transaction malleability, which was critical for Lightning’s security
- Increased effective block size, reducing on-chain fees for channel operations
2. Taproot
- Activated in November 2021
- Improves privacy and efficiency for complex transactions
- Reduces the footprint and cost of Lightning channel operations
- Enables more sophisticated contract structures
3. Proposed Future Upgrades
- SIGHASH_ANYPREVOUT: Would enable Eltoo, a simplified Lightning channel construction
- Schnorr Signatures: Already part of Taproot, enabling more complex multi-signature schemes
- Covenants: Would allow more sophisticated control over how Bitcoin can be spent
The Future of Bitcoin Scaling
1. Interoperability
- Cross-Implementation Standards: Better compatibility between different Lightning implementations
- Layer 2 Interoperability: Communication between different scaling solutions
- Cross-Chain Capabilities: Lightning-like networks across multiple blockchains
2. Advanced Applications
- Streaming Payments: Pay-per-second or pay-per-byte services
- Decentralized Exchange: Non-custodial trading using Lightning
- Content Monetization: Micropayments for content consumption
3. Technical Advancements
- Channel Factories: Reducing the on-chain footprint of channel creation
- Eltoo: A proposed update to Lightning’s channel mechanism for simpler state management
- Dual/Multi-Funded Channels: Allowing both parties to contribute to channel funding
Getting Started with Lightning
For Users
- Choose a Lightning Wallet: Options include Breez, Phoenix, Muun, or BlueWallet
- Acquire Bitcoin: Purchase or receive Bitcoin to your Lightning wallet
- Open Channels: Many modern wallets handle this automatically
- Make Payments: Experience fast, low-cost Bitcoin transactions
For Merchants
- Lightning Payment Processors: Services like BTCPay Server, Strike, or OpenNode
- E-commerce Plugins: Integration options for popular platforms
- Point-of-Sale Solutions: Hardware and software for physical retail
For Developers
- Lightning Development Kits: LDK, Polar, or Lightning Terminal
- API Documentation: Resources from LND, c-lightning, or Eclair
- Testing Environments: Simulated networks for safe experimentation


